
Article
The article categories in an agriculture website encompass a wide range of topics relevant to the agricultural industry. These categories often cover areas such as crop cultivation techniques, livestock management, agricultural machinery and technology, organic farming practices, soil health and fertility, pest and disease management, agricultural economics and markets, agricultural policy and regulations, sustainable agriculture, climate-smart farming, and agricultural research and innovation. These categories serve as a repository of valuable information and resources for farmers, agronomists, researchers, and individuals interested in various aspects of agriculture.
Safeguarding Wetlands for Conserving Biodiversity of Nepal – By Swikriti Panthi || Krishi Vines
INTRODUCTION According to RCS (2019), wetlands are defined globally as those regions that are continuously or periodically submerged in water up to a maximum depth of six meters. Nepal’s wetland hosts 42 globally threatened species (IUCN red list 2002) and are valuable from an economic, ecological, aesthetic, sociocultural, and religious standpoint. They are found in…

Impact of Climate Change on Agro-Biodiversity in Nepal – By Samraksha Ghimire || Krishi Vines
Introduction Nepal, with its diverse topography and climate, hosts a rich array of agro-biodiversity. This diversity includes various crops, livestock, and traditional farming practices that have evolved over centuries. However, climate change poses significant threats to this invaluable resource. Rising temperatures, erratic rainfall patterns, and increased frequency of extreme weather events jeopardize agricultural productivity and…

How Monoculture is Threatening Agrobiodiversity and Our Future ? – By Upendra Bhusal || Krishi Vines
Introduction In fields across the world, a quiet but dangerous trend is spreading. As far as the eye can see, rows upon rows of identical crops dominate the landscape—fields of corn, wheat, rice, or soybeans stretch endlessly. This practice, known as monoculture, involves growing the same crop year after year on the same land. While…

Innovations in Irrigation Techniques for Small-Scale Farmers in Chitwan – By Avishek Rimal || Krishi Vines
Introduction For small-scale farmers in Nepal, especially in the Terai region where irrigation is crucial to agriculture, one of the biggest concerns is managing water resources. Smallholder farmers in Chitwan, which is renowned for its fertile soil and varied crop output, frequently clash with water scarcity and ineffective irrigation infrastructure, which reduce agricultural productivity. The…

“Assessing the Impact of Climate Change on Rain-Fed Agriculture and Flash Floods in Nepal” – By Shahil Baral || Krishi Vines
IntroductionNepal relies heavily on agriculture, with more than 60% of its population depending on farming. The majority practice rain-fed agriculture, which is particularly vulnerable to climate change. Recent shifts in weather, such as inconsistent rainfall and more frequent flash floods, are beginning to disrupt traditional farming methods (Ministry of Agriculture Development, 2019; ICIMOD, 2021). These…

Tigers on the Move: Climate Change, Habitat Loss Push Nepal’s Big Cats to Higher Altitudes || Khusiram Lamsal
Tiger populations have faced significant declines in recent years due to poaching, dwindling prey, and habitat loss. However, among the humid evergreen forests, dry open jungle, and grassy swamps of southern Nepal, tiger populations are growing. Climate change threatens this progress. Hotter temperatures, increased flooding, and prolonged dry spells are expected to endanger existing tiger…

Bhakimli Farmers Launch Commercial Akabare Chilli Farming – By Upendra Bhusal || Krishi Vines
Farmers in Bhakimli, Beni Municipality-3, Myagdi, have initiated the district’s first commercial-scale cultivation of the Akabare (Dalle) variety of chili peppers. According to Sanjeev Bastola, the head of the Agricultural Knowledge Center Myagdi, both individual farmers and farmer collectives in Bhakimli are now engaged in the systematic cultivation of Akabare chilies. He highlighted the region’s…

Details Study of Lumpy Skin Disease || Krishi Vines
Lumpy Skin Disease (LSD) is a non-zoonotic viral infection that mainly affects cattle and is uncommon in buffaloes. It was first reported in Zambia in 1929, and primarily thought to be the result of poisoning or hypersensitivity reaction to insect bites. The cause was later identified as Lumpy Skin Disease Virus (LSDV) after the viral…

“Managing Locust Swarms: Sustainable Approach Revealed to Protect Wildlife and Human Health”
According to recent studies in agronomy, conventional insecticides caused harm to regional bird and honeybee populations during a recent locust outbreak in the Horn of Africa. But Somalia chose a remedy that can control swarms while safeguarding human health and wildlife. The findings point to a strategy for locust management that is sustainable. According to…

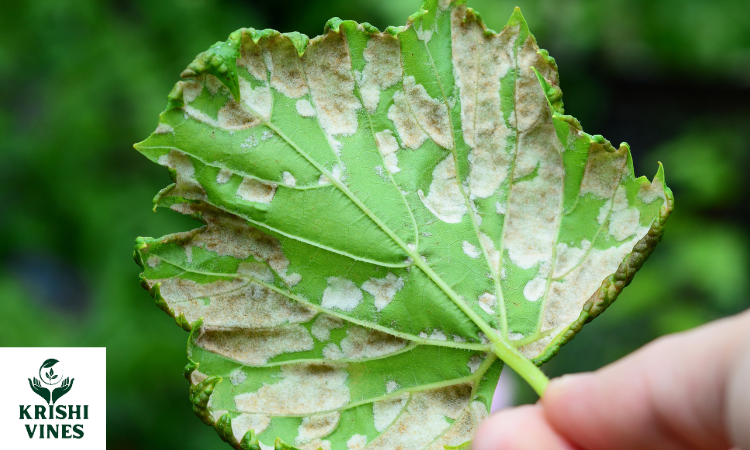
Downy Mildew of Crucifers || Peronospora parasitica || Crop Diseases and their management
Downy Mildew of Crucifers: This disease is found all over the world where crucifers are grown. It affects a wide range of hosts i.e. turnip, cauliflower, Sarson, radish, cabbage etc. Etiology: It is caused by the Peronospora parasitica, P. brassicae. The main difference with Downy Mildew of cucurbits is that it doesn’t form zoospores…


